What is the current fashion in the global laser market? If you run a factory focusing on material processing, your first answer is probably fiber laser. And expectedly you might be planning to order one to escalate your production line. They are used in fiber laser cutters, laser markers, laser depanelling systems and more. But wait, is there any must-knows about fiber lasers? In this article we will look into the 7 key advantages of fiber lasers. We will also compare them with other commonly used laser types. Here is what we will cover:
Optical fiber is both the gain medium and resonator of a fiber laser
7 Advantages of Fiber Lasers
Before buying a fiber laser, it is necessary to make clear what unique features distinguish it from other lasers. As we know, a workable laser needs three components: the pumping source for the energy supply, the gain medium, and the optical resonator. For fiber lasers, while the choices of pumping sources are unsurprisingly between laser diodes and other fiber lasers, the designs of the gain medium and optical resonator are fundamentally different. This unique structure gives rise to 7 key advantages:
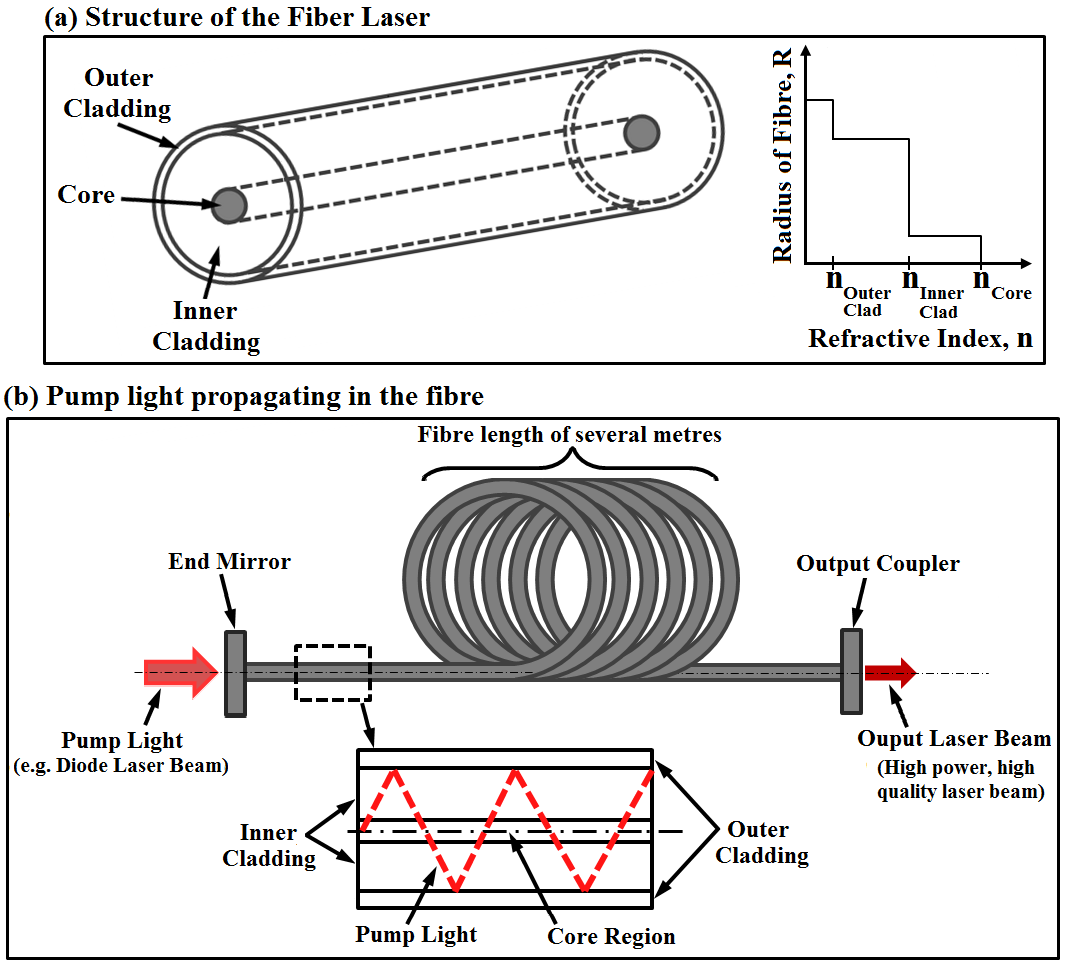
Schematic illustration of a simple fiber laser cavity. A fiber of several meter in length is enveloped between the end mirror and the output coupler forming the laser cavity. Courtesy of Catherine Wandera as seen in the book “Fiber Lasers in Material Processing“
1. Highly Efficient Gain Medium
Unlike other lasers, fiber lasers achieve light amplification in optical fibers, which are doped with rare earth metal ions such as ytterbium (Yb3+), neodymium (Nd3+), thulium (Tm3+), praseodymium (Pr3+), or erbium (Er3+). These laser active ions can absorb most of the pump light, and then emit photons with characteristic frequencies via stimulated emission. The inherently flexible structure of fibers enables using much longer gain distances than other laser types. This provides a high optical gain.
2. Smart Feedback Loop through Fiber Bragg Gratings
Instead of using the conventional dielectric mirrors, the optical feedback in fiber lasers is usually provided by fiber Bragg gratings, a series of glass fibers with different refractive indices fusion-spliced in a periodic manner. These periodic structures can reflect the laser beam at certain wavelength and hence become the optical cavity of the fiber laser. Thus, for a fiber laser, the optical cavity is actually inside the gain medium.
3. Robust Optical Cavity
When talking about fiber lasers, one common pitfall to avoid is that fiber lasers are not equivalent to the lasers that have optical fibers. In fiber-coupled diode lasers for example, optical fibers are employed only for beam delivery purposes and do not involve in the physics of stimulated emission. Hence, although optical fibers are indeed coupled with the laser systems, they still do not have all the superior qualities of a fiber laser. The unique integrated optical cavity with coiled fiber as the gain medium creates a robust and stable optical cavity.
4. Compact Footprint
One of the key advantages of fiber lasers is their compact layout. Compared with their rivals they sport a much smaller footprint at comparable output powers. This is because optical fibers are bendable and can be coiled into compact spaces. Furthermore, the flexibility of optical fibers also make possible further customization of the optical path, giving more freedom in design for various specific situations.
5. High Output Power
Since the gain medium in fiber lasers are very thin and flexible, it is possible to have the optical fibers several kilometers long, and hence reach a very high gain of the pumping light. Also, due to the large surface area to volume ratio of optical fibers, the heat generated by fiber lasers can by efficiently dissipated. Thus, fiber lasers can function continuously at kilowatts levels without the need for sophisticated cooling systems.
6. Excellent Beam Quality
Normally, laser beam quality is interpreted as a measure of how tightly the beam can be focused, and it is quantified by an M2 factor, which is ideally equal to 1 for the highest beam quality. In a fiber laser, single-mode fibers typically offer the best beam performance, and can hence conceive significant applications. For instance, in laser cutting and welding, a high beam quality will allow for a long distance between the workpiece and the focusing object. This configuration will protect the optics from the debris and fumes. Most importantly, the reduced beam diameter can not only make possible finer structure manufacturing, but also the use of smaller and cheaper optical components.
7. High Reliability
Fiber lasers are of high reliability and almost maintenance-free, and since the optical path is enclosed within protective cladding layers, the laser beam is less susceptible to exterior disturbance. Thus, fiber laser usually boast excellent stability in high-temperature and vibrational working conditions.
What is the difference between a fiber laser and other lasers?
While the advantages of of fiber lasers are numerous, it is important to understand how they stack up against competition. As we will see below the superiority of fiber lasers is a function of the application setting and their rivals can be more suitable in certain circumstances.
Fiber Laser vs Bulk Laser
Bulk lasers are a type of solid-state lasers that use doped bulk crystal or glass as the gain medium, and two good examples are Nd: YAG laser and Ti sapphire laser. Generally, fiber lasers exhibit better specs than bulk lasers, as seen in the chart below:
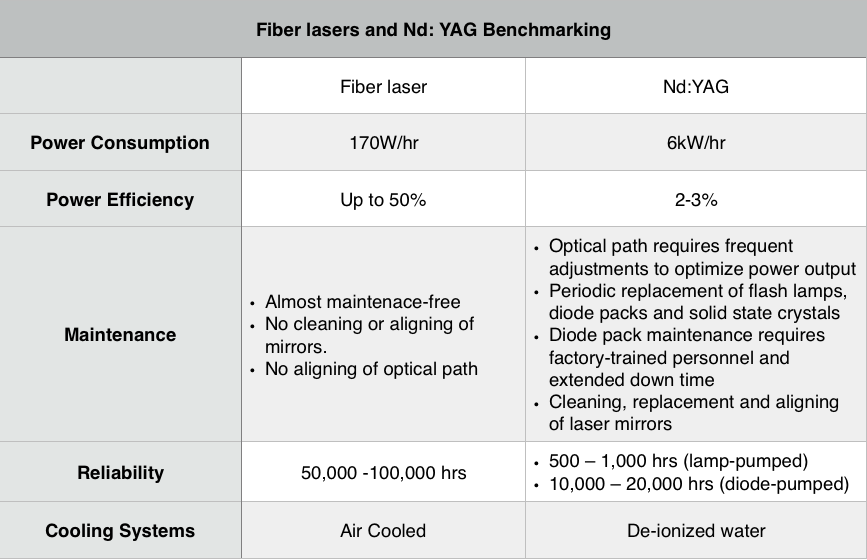
Benchmarking with Nd:YAG diode-pumped solid state laser. (Courtesy of Laser Photonics).
However, this does not mean that bulk lasers have no value for material processing. For example, in wavelength region of 700-1000 nm, no fiber laser can substitute the tunable Ti sapphire. In addition, bulk lasers can reach higher peak power, and are therefore more suitable for processing materials. Most importantly, fiber laser systems may require special components and complicated using methods, and its higher cost may be unfavorable economically.
Fiber Laser vs CO2 Laser
While both types of lasers are very suitable for cutting materials, they actually have different functional emphasis. On one hand, CO2 lasers are very suitable tools to cut non-metallic materials such as plastics. Their relatively high efficiency and good beam quality make them the most widely used laser type in this industry.

A laser cutting machine slicing through a sheet of metal. Courtesy of Nukon.
On the other hand, fiber lasers have gained significant progress in cutting metal sheets (mainly stainless steel) in recent years, primarily due to their high cutting speed, which is often 2-3 times faster than CO2 lasers at the comparable power levels. Generally, when cutting metals with thickness of 0.25” and thinner, it is worth considering fiber lasers for mass production, but when the metal is thicker than 0.375”, CO2 lasers still enjoy the speed advantage and superior cutting qualities. Thus, it is unlikely for fiber lasers to completely replace the CO2 lasers for material cutting.
Fiber Laser vs Direct Diode Laser
Diode lasers have long been accused of low output power and poor beam qualities. Nevertheless, recent research progress in direct diode laser techniques has exhibited its potential as a “big player” for material processing. Compared to fiber lasers, direct diode lasers can allow for 10%-20% improvement in cutting speed. Also direct diode lasers can cut thick metals and achieve smaller surface roughness. Most importantly, they are also suitable for processing highly reflective materials such as copper. In contrast, fiber lasers exhibit restricted effectiveness here. However, fiber lasers are still enormously advantageous in terms of beam quality and technology maturity. This makes them perfect choices for macro material processing.
Summary
Fiber lasers have clearly revolutionized the laser industry. They offer a number of key advantages over other laser types, opening avenues for increased production efficiencies. The choice of highly efficient gain medium and integrated laser cavity offer a robust and stable output performance. Their compact footprint is a key selling point for OEM / integration applications. Nonetheless, their superiority is highly dependent on the application setting, mindful of their output wavelength and limited tunability.
Did you know that FindLight marketplace has a rich category of fiber lasers from a variety of suppliers. If you liked this article, you might also be interested in our Advanced Guide on Tunable Diode Lasers.
Today's post was sponsored by DataRay Inc. - masters of laser beam profilers

It’s nice that you pointed out how fiber lasers are of high reliability and almost maintenance-free. I was watching a TV show yesterday and I learned about the usefulness of fiber laser cutting. Also, it seems fiber laser cutting devices are widely available now, which sounds very convenient.