The development of laser technologies in recent decades has uncovered a vast range of marking and engraving applications. Ranging from aerospace implementations to usage for more personal projects, laser engraving and marking technology has revolutionized a wide variety of engineering industries. In this blog post, we will discuss the evolution of laser marking and engraving technologies. Starting with their inception, to their current applications for modern projects.
Before we move on a few important technological terms to know:
- Flash Tube: an electric arc lamp used to create continuous full-spectrum white light.
- Flash Lamp: produces light much like a Flash Tube, but produces smaller consecutive flashes of light and is more dependent upon the current density.
- Output Coupler: a partially transparent mirror that allows certain portions of the laser beam to exit the optical resonator.
- PCB: printed circuit board; generally a non-conductive panel with conductive lines etched into it.
The First Laser Technology
Laser engraving and marking have been around for several decades, with eventual utilization for things we see in day-to-day life. The first working laser was created in 1960 by American Engineer Theodore Maiman at the Hughes Research Laboratory in California. Maiman’s laser, coined the ruby laser, was a solid-state type laser that utilized a ruby crystal as its medium. It was the first known laser to produce a singular, narrow beam of coherent light, making it possible to amplify desired light waves without spreading them out.
The machine’s ruby crystal was a cylinder of synthetic ruby with silver-coated ends as shown in the diagram below. The crystal was composed of aluminum oxide and chromium atoms. Maiman experimented with two different pump sources during his creation of the laser: a flash lamp and a flash tube. Once the light from the flash tube/lamp is shone on the end of this crystal, the atoms become excited, causing them to emit light. This emitted light is reflected repeatedly through the crystal by mirrors that line the optical cavity. The amplified light is concentrated and finally transmitted through the output coupler to exit as a laser beam.
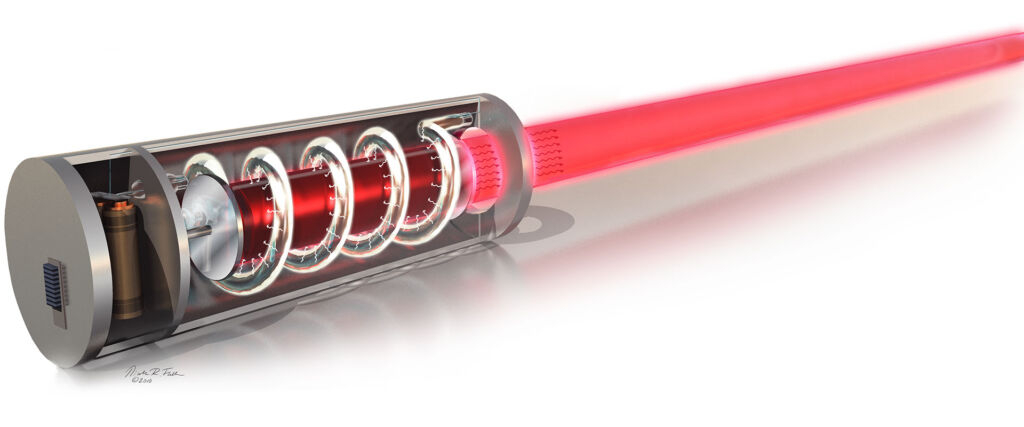
The ruby laser, so named because of the ruby crystal used, was the first working laser. Laser technology has since advanced, and has many modern technologies possible, from cutting-edge surgeries to DVDs and computers. Courtesy of Sayo Studio
First Use of Laser Engravers
Engraving and marking methods were first used nearly a decade after the first laser was developed in 1960. It became a popular practice and practical tool in numerous manufacturing industries in the 1970s. One of the earliest documented laser “etching” projects was in the production of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Laser engraving was used to etch circuits onto the boards with unbeaten precision, allowing for the production of more complex – yet also compact – electronic devices. Laser etching is one of the most important aspects of PCB production and manufacturing, as it involves the removal of copper from the board to create any desired circuit pattern. During this laser etching procedure, all copper is removed from the board with the exception of the circuitry, which is preserved under a tin plating.
Aside from PCB engraving, another original use of laser engravers was for cutting and drilling applications. They were used to cut and drill holes through various materials that tend to be difficult to work with using formerly traditional methods. This includes plastics, wood, and certain types of metals. The focused beam of laser light is able to vaporize or melt materials, allowing the machines to drill precise holes with extreme accuracy. Comparatively, this was perfect for difficult projects that had minimal tolerance and very little room for error.
Applications of Laser Marking and Engraving
Laser machines have evolved to versatile tools for material processing in a number of different industries. The following is just a partial list of areas where laser markers and laser engravers have become a common tool in the production process.
General Manufacturing
In the 1980s and 90s, laser engraving/marking technologies became more widely available to other industries. Manufacturers began to utilize these systems to mark components with serial numbers, barcode labels, and other information to assist in the identification and organization of units. They were also used to engrave complex patterns and designs into surfaces. This provided a new method of customization for companies that wished to display logos or other branding elements on products. A major advantage of this type of branding comes from the high quality of permanent laser markings, which consequently are very resistant to fading or wear. Presently, laser markers and engravers are preferred in manufacturing for these same reasons and benefits.
Aerospace & Automotive
Similarly, laser marking is oftentimes used in the aerospace industry to easily label components and products. This allows for better traceability and quality control in assembly procedures. Information engraved on aerospace parts can be used to track the movement and performance of components throughout the supply chain, ensuring that all parts meet the high standards required in all aspects of the aerospace industry. These same applications are used in the automotive industry as well, where laser markers are a very ideal tool for component identification. Alphanumeric, barcodes, and data-matrix codes are engraved on nearly every material used in automotive manufacturing, from design/development to the final assembly.
Laser Marking and Engraving in Bottling Industry
Additionally, this technology has become very prominent and popular in bottling production lines. The most common use of laser engraving in the bottling industry is to add logos, branding elements, and other customized designs to plastics or glass. Aside from decorative applications, laser engraving is also used in the bottling industry for functional purposes. Expiration dates, batch numbers, and other identifying information can be marked onto specific bottles as desired. This, much like applications in other industries, is very useful for product quality control.
Project Engraving
All things considered, easier access to laser engraving technology has permitted a new range of applications in more personal projects. The possibilities are seemingly endless for customized laser engravings, with almost no restrictions on complex designs and extensive material compatibility. The systems can be used to engrave medals and awards, or even to create customized décor or products. Small businesses can use this technology to create personalized products for customers, offering unique and custom designs. Although the availability of this technology doesn’t stop there thanks to its reputable user-friendliness. Individuals with personal machines can easily complete at-home projects, and create personalized gifts for friends or family. A few of these many examples are showcased below.
If you’re interested in purchasing one of these machines for business or personal purposes, you can start your comparison shopping with our dedicated set of Laser Engraving categories.
You might also want to check out our Guide to Laser Scanheads.




The article effectively highlights the key advancements in laser marking techniques and showcases the wide range of industries benefiting from this innovative technology. The well-structured content, supported by detailed explanations and real-world examples, makes it a valuable resource for anyone seeking to grasp the significance of laser marking and engraving in today’s industrial landscape.
This blog provides a comprehensive overview of the evolution of laser marking and engraving technologies, detailing their applications in aerospace and personal projects. It effectively captures the transformative impact these innovations have had across diverse engineering industries.