
Advancements in fiber optic technology have transformed modern methods of data transport and communication. Courtesy of uSwitch.
Introduction
While often considered a rather new technology, the concept behind fiber optics has actually been around since the 1840’s, when Swiss physicist Daniel Colladon discovered he could shine light along a water pipe. The water was able to carry the light down the pipe because of a phenomenon called internal reflection, one of the driving concepts behind present day fiber optic technology. Today, fiber optics works near the speed of light and is able to send billions of bits of data across the world.
Fiber optics refers to the medium and technology associated with the transmission of data as light travels along a glass or plastic strand or fiber. This information can be sent over incredibly long distances and at impressive speeds. For example, one fiber optic strand can carry huge amounts of information, such as tens of thousands of telephone calls. With each strand measuring less than a tenth the width of a single human hair, fiber optic cables can contain anywhere from two to several hundred fiber optic strands, easily carrying several million calls. This technology has truly transformed modern methods of data exchange and the way people communicate.
How it Works
Generally speaking, fiber optic cabling is similar to a very long, flexible pipe. Imagine that this pipe is covered with perfect mirrors on the inside and that you are looking into one end. Several miles away at the opposite end, someone shines a light into the pipe. Even with twists and turns in the pipe, you can see the light due the fact that the inside is a perfect mirror. This example represents the concept of internal reflection.
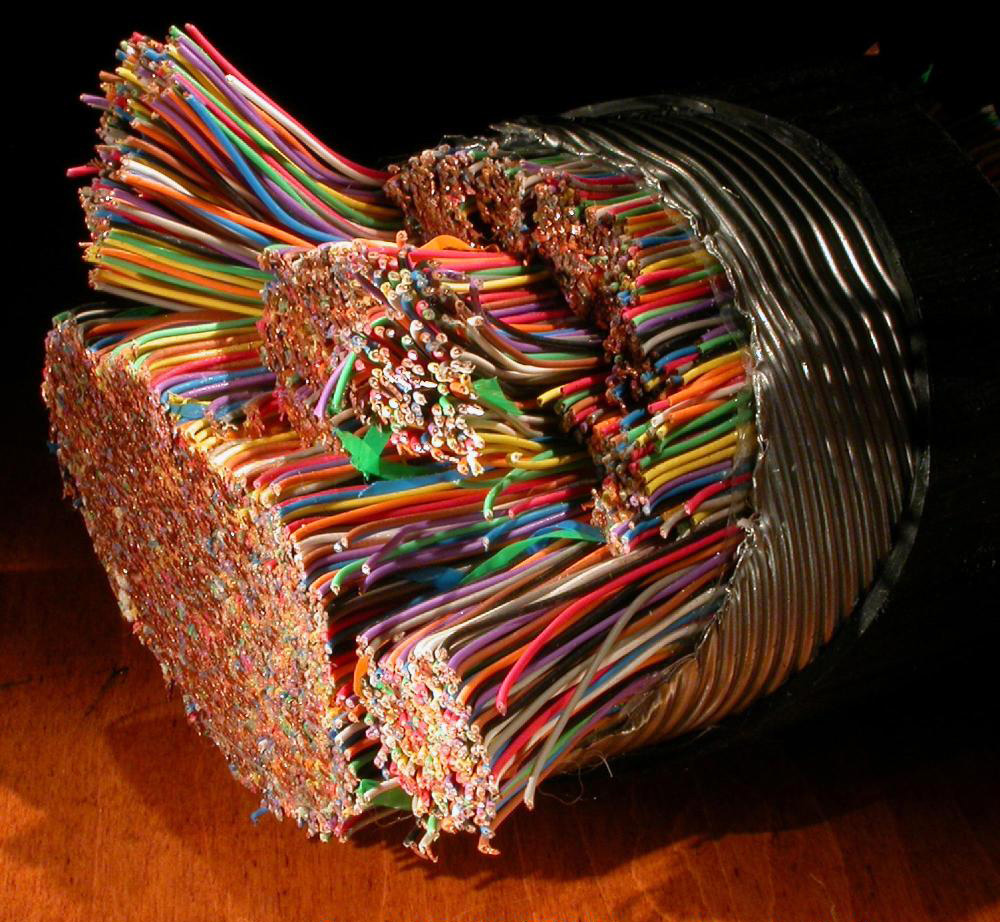
Many fiber optic cables include several thousand individual optical fiber strands. Courtesy of Extreme Tech.
Similar to the pipe, the light in a fiber optic cable travels through thin glass in the center of the fiber called the core. The cladding, or the outer optical material surrounding the core, is homologous to the perfect mirror. This component, which is typically made of glass or plastic, ideally will not absorb any light from the core. This allows the light waves to travel for great distances.
When fiber optics is used in telecommunication systems, several different components are included to compose a fiber optic relay system. The main components include a transmitter, an optical regenerator, and an optical receiver. The transmitter is responsible for producing and encoding the incoming light signals. It directs the optical device to either turn the light “on” or “off” in a specific signal, thus generating a signal. An optical regenerator boosts the light signal after long distances, due to inevitable signal degradation. Lastly, an optical receiver uses a photocell or photodiode to receive and decode the light signal, and sends the signal to devices like computers, TV, or telephones.
Advantages of Fiber Optics
The exponential increase in the integration of fiber optics is due to a variety of different advantages. Particularly, it is less expensive, thinner, more flexible, and has a higher carrying capacity than its metal wiring competitors.
One of the main advantages of fiber optic cables are that they are less expensive than traditional metal wiring. Manufacturing optical cables is generally cheaper, saving cable, TV, and internet providers money as well as the consumer.

The thin, lightweight, and flexible nature of optical fibers is crucial in a variety of fields. Courtesy of News Medical Life Sciences.
Another major advantage is that they are thinner, more flexible and more lightweight. These characteristics make them easier to handle and transport. Thanks to this quality, they can be wrapped into bundles, thus resulting in a higher carrying capacity. This allows for more phone lines in the same cable or channels into a TV. In fact, they are so lightweight that NASA even uses fiber optic cabling in their space shuttles to decrease the overall weight. Their flexibility, on the other hand, makes them ideal in applications like medical imaging and plumbing.
Furthermore, signals traveling along fiber cables experience less signal loss than in metal wires. Even though light and electricity travel at the same speed, fiber cables are much more efficient, as signals do not degrade nearly as quickly. Typically, the greater the distance, the lower quality the signal. However, because the signal does not degrade as rapidly, fiber optic cables require fewer sub-stations to maintain quality. This corresponds to a lower infrastructure investment and again, a less expensive technology.
Future of Fiber Optic Technology
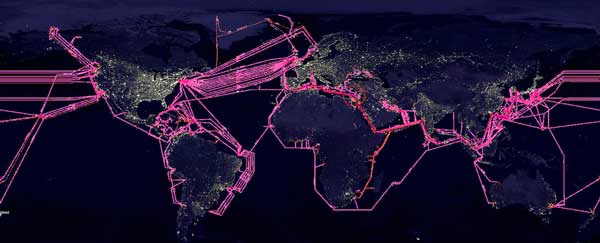
Countries around the world are turning to fiber optics for a reliable source of telecommunication. Courtesy of The Fiber Optic Association.
Because of the widespread advantages, many countries are turning to fiber optics for a reliable source of telecommunication. Whereas South Korea, Japan, and Singapore are on the forefront of this technology, developing countries are also realizing just how important it is to have fast, reliable, internet for their economic growth. Consequently, some nations have even given high-speed networks a higher priority than the implementation of transportation infrastructure.
In the United States, experts predict that fiber optic networks will also grow significantly within the next few years. With an anticipated worth of 5.00 Billion USD by 2021, the fiber optics market has many backers. For example, Google Fiber is one of the first large scale projects aiming to refurbish current internet networks. The goal of this project is to provide a network producing 1 gigabit per second speed, a value nearly 100 times faster than what most Americans currently have.
In addition to telecommunications, fiber optics also finds application in military, medical, automotive, and aerospace, just to name a few. The advantages offered by fiber optic technology appeal to a diverse mixture of industries, consumers, and investors. Needless to say, the fiber optic technology industry holds a bright future.
For even more information on how fiber optic cables work consider this animated guide – courtesy of The Bookmark, a technology-focused blog that features educational content.





Fiber optic cables are cables that contain strands of glass fibers inside of an insulated casing. These cables are capable of delivering high-performance telecommunications amongst other things. Thanks for sharing this and looking forward to it.
Wow, it’s interesting that there are cases when high speed internet connection is being prioritized over transportation infrastructure. I intend to start looking for a work-from-home job soon so I’m going to need fiber optic cables to ensure a fast connection. This way, I can comfortably be able to attend to my children’s needs while also earning income to help with spending.
From this article you will get to know about the fiber optic technology. This article gives suggestions on limitations and delimitation of such selection. I enjoyed reading while going through this article and this is the best link for gaining all the information about it. Found an another website nexttelecom.co.nz/products/ip-telephony-and-voip it has lots of valuable information for everyone.
Yes, you are right thanks for sharing this information.
Superb insights! Fiber optic cables have indeed become a cornerstone in contemporary technology. Their remarkable capacity for high-speed data transfer and minimal signal loss make them a preferred choice. What’s impressive, as you noted, is their resilience even in extreme environments, which showcases their versatility and reliability. Your explanation provides a clear and succinct overview of the intricacies of fiber optic technology, and highlights its pivotal role in the telecommunications and data networks that underpin our modern world.