Glan Laser Polarizers are engineered to achieve high polarization purity and minimal light scattering in demanding laser applications. This white paper details the operational principles, construction, and performance characteristics of Glan-Laser polarizers, which utilize select-grade calcite prisms designed for high damage thresholds and broad wavelength compatibility. Aimed at optical engineers, this article elucidates technical specifications, comparative advantages, and practical applications, providing essential knowledge for the development and optimization of sophisticated optical systems.
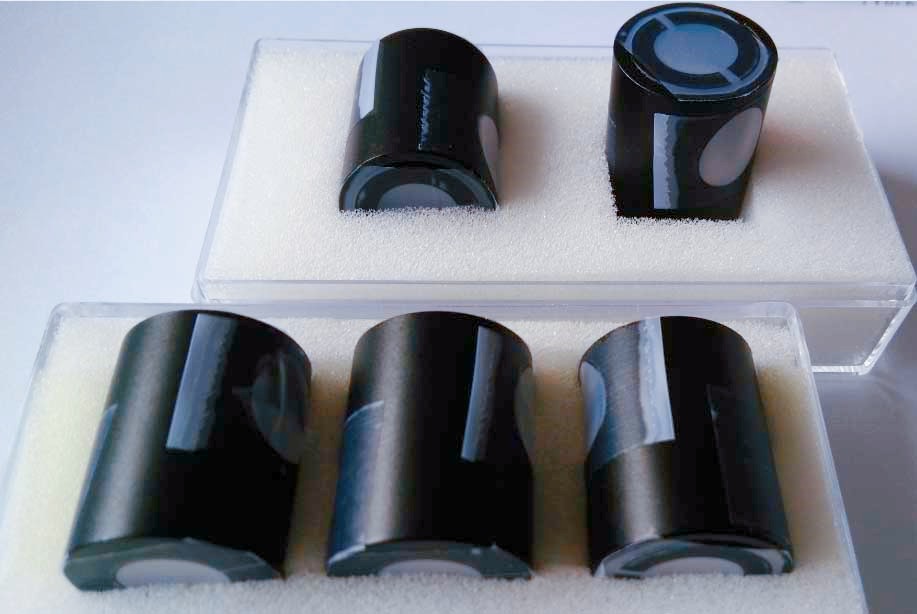

Glan-Laser polarizers displayed in an open box, precision-engineered air-spaced prism structures for high-power applications.
This white paper is brought to you by LECC Technology - Pioneering Laser Technology for Global Innovation for over 20 years.
1. Introduction
Polarization, the orientation of light waves along particular planes, is fundamental to managing light propagation and its interactions with materials in optical technologies. In precision applications ranging from quantum computing to advanced spectroscopy, the control of light polarization directly influences efficiency, accuracy, and performance. Glan Laser Polarizers, known for their high extinction ratios and minimal light loss, stand as critical components in achieving precise polarization control.
These polarizers utilize air-spaced calcite prisms, a design choice that enhances their capability to handle high-energy laser beams while maintaining high polarization purity. This design effectively reduces photon absorption and scattering, factors that can compromise the integrity of the polarized light in sensitive optical setups.
The operational efficiency of Glan Laser Polarizers is not just a function of their material or design. It is also a reflection of their evolution to meet the rigorous demands of modern optical systems. Whether integrated into laser surgery equipment or utilized in the photonic research laboratories, these polarizers ensure that light can be manipulated with high precision, providing the reliability required for cutting-edge applications.
In this article , we explore the design, functionality, and application of Glan Laser Polarizers, elucidating their role in advancing optical engineering by enabling detailed control over light properties. Through this guide, optical engineers will gain comprehensive insights into optimizing these polarizers in various demanding environments, ensuring optimal performance in their respective fields.
2. Principles of Operation
2.1. How Glan Laser Polarizers Work
Glan Laser Polarizers operate based on the principle of double refraction in birefringent materials — primarily calcite. Calcite is a naturally occurring crystal that possesses two distinct indices of refraction for two orthogonal polarization directions: the ordinary ray (o-ray) and the extraordinary ray (e-ray). When unpolarized light enters a Glan Laser Polarizer, it is split into these two polarized rays. The design of the polarizer ensures that only the e-ray, which is the desired polarized light, is transmitted through the polarizer, while the o-ray is reflected and discarded.
This selective transmission is achieved by orienting the calcite crystals so that the optical axis is parallel to the plane of incidence. As light passes through the air gap between the two prisms of the polarizer, total internal reflection occurs at the interface. This reflection effectively blocks the o-ray by directing it out of the polarizer at an angle, while the e-ray continues straight through the device due to its alignment with the optical axis (see illustration below).
2.2. Key Design Features and Materials
The primary material used in Glan Laser Polarizers is high-grade, laser-quality natural calcite, chosen for its low scatter and high birefringence properties. The quality of the calcite is crucial as it directly affects the polarizer’s extinction ratio and overall optical performance. The prisms are precisely cut and aligned to maximize the efficiency of the polarizing effect and to handle high-energy laser beams without degrading.
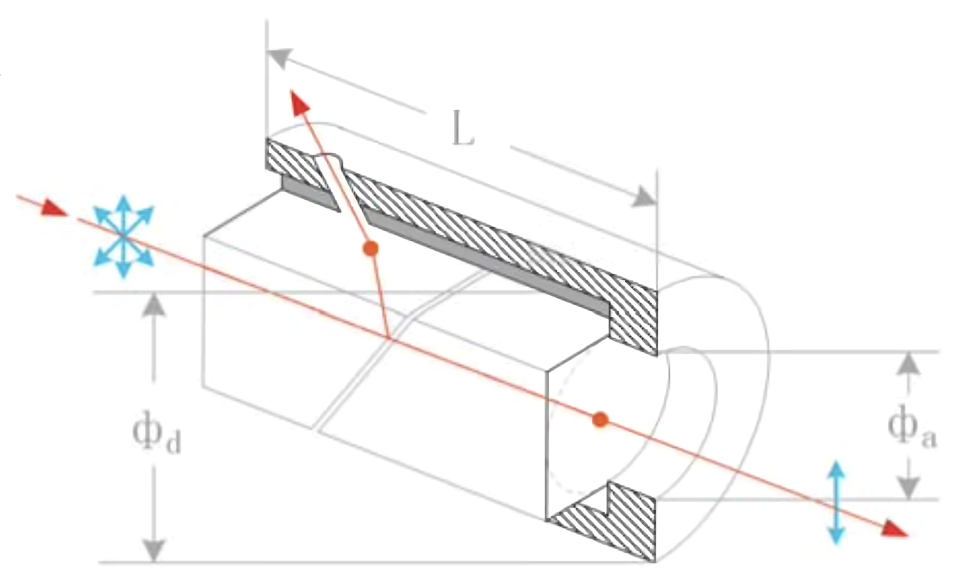
This schematic illustrates the internal configuration of a Glan Laser Polarizer, highlighting the calcite prisms, air gap, and the paths of polarized light rays. Image courtesy of Union Optics – as appears on FindLight.
The air gap between the calcite prisms is another critical design feature. Unlike designs where the prisms are cemented together, the air-spaced configuration in Glan Laser Polarizers minimizes the potential for thermal damage and absorption at high laser powers. This design not only enhances the durability of the polarizer but also significantly improves its performance by reducing the likelihood of optical distortions.
The surfaces of the prisms are polished to a 20-10 scratch-dig finish, a standard in the industry for high-quality optical components. This high level of polish ensures minimal scattering and absorption of the transmitted e-ray, which is essential for applications requiring high precision and minimal light loss.
Furthermore, these polarizers can be equipped with various anti-reflection (AR) coatings tailored to specific wavelength ranges. These coatings are applied to the input and output faces of the polarizer to enhance transmission efficiency across the designated spectral range. The choice of coating depends on the application’s specific needs, ranging from ultraviolet to near-infrared light wavelengths.
3. Types of Glan Laser Polarizers
The selection of an appropriate Glan polarizer hinges on understanding their distinct designs and the specific requirements of the application in terms of power handling, wavelength range, and polarization purity.
3.1. Glan-Thompson Polarizers
Design: These polarizers use two calcite prisms that are cemented together along their entire length. This traditional design allows for a broad field of view and excellent wavelength versatility but limits the polarizer’s ability to withstand high-power laser beams.
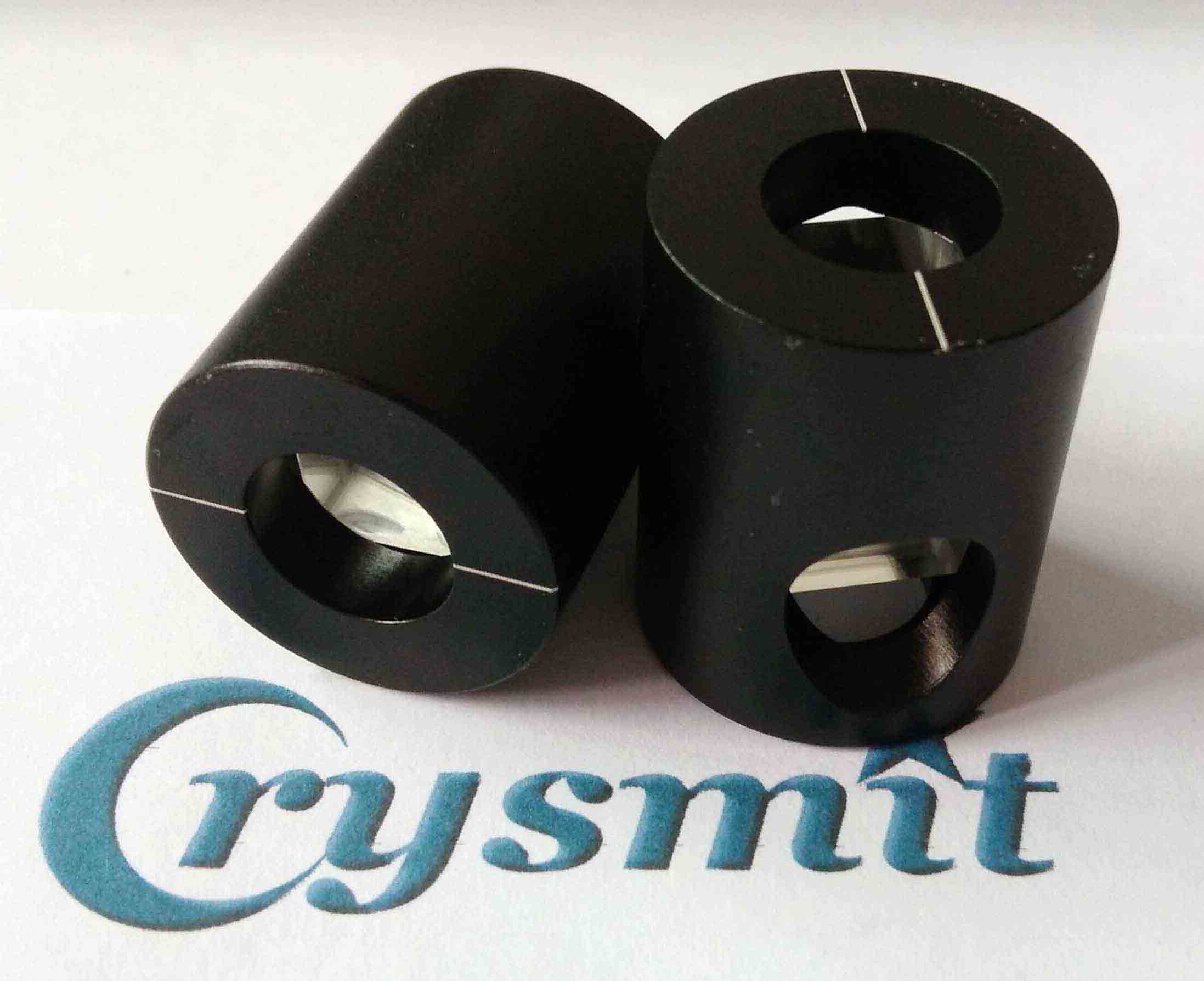

A typical Glan-Thompson Polarizer. Photo courtesy of Crysmit Optics – Link to the actual product.
Performance: Glan-Thompson polarizers provide good extinction ratios and are suitable for lower power applications. The cemented interface, while reducing the potential for internal reflections and absorption, is prone to damage under high-power conditions.
Applications: Ideal for educational purposes, routine laboratory use, and photographic equipment where high power handling is not required.
3.2. Glan-Taylor Polarizers
Design: Similar in concept to Glan-Laser polarizers, Glan-Taylor polarizers feature two air-spaced calcite prisms. The key difference lies in their slightly less aggressive approach to power handling, making them more suitable for moderate to high-power applications but not the highest as with Glan-Laser.
Performance: These polarizers are highly effective at providing high extinction ratios while maintaining beam quality. They can handle significant power levels but fall short under extreme conditions compared to Glan-Laser types.
Applications: Commonly employed in scientific research and industrial applications that require precise polarization control without the extremities of power that challenge Glan-Laser polarizers.
3.3. Glan-Laser Polarizers
Design: Glan-Laser polarizers are constructed with an air-spaced configuration similar to Glan-Taylor polarizers but are further optimized to enhance their resilience against high-energy impacts. This optimization includes precision alignment of the calcite prisms and the strategic placement of the air gap to maximize the angle of total internal reflection. This alignment minimizes the optical path within the material, reducing the potential for heat accumulation and damage under intense laser operation.
Performance: The specific engineering adjustments in the prism alignment and air gap placement allow Glan-Laser polarizers to achieve exceptionally high damage thresholds. They are designed to handle the most extreme power densities by minimizing absorption and thermal effects, which are critical factors in high-energy laser applications. This results in a polarizer that can sustain high levels of power without compromising the quality of the polarized light.
Applications: Glan-Laser polarizers are indispensable in settings that demand robust performance under extreme conditions. This includes laser fusion research, high-powered laser cutting and engraving, and military applications where laser systems must operate reliably at high intensities.
4. Performance Characteristics
Glan-Laser polarizers stand out for their exceptional performance across several key metrics: extinction ratio, wavelength range, and damage threshold. These polarizers consistently achieve an extinction ratio exceeding 100,000:1, ensuring high purity in the transmitted polarized light with minimal leakage. They are designed to operate over a diverse wavelength range, from ultraviolet to near-infrared, catering to a wide array of optical applications.
A standout feature of Glan-Laser polarizers is their high damage threshold, which is crucial for their use in high-energy environments. Typically, these polarizers can withstand energy densities up to 10 GW/cm², a capacity that significantly surpasses that of other polarizing technologies such as cube or film polarizers. This high damage threshold is primarily attributed to their air-spaced design, which minimizes heat accumulation and enhances durability under intense laser operation. Compared to other polarizers, Glan-Laser polarizers offer unmatched durability and performance stability, making them ideal for demanding applications where precision and long-term reliability are important.
5. Advantages of Glan Laser Polarizers
Glan Laser Polarizers offer unmatched durability and precision in high-energy laser applications. Their air-spaced design prevents thermal stress and eliminates degradation common in cemented or film polarizers, making them essential for applications that demand consistent polarization under extreme laser power. Unlike wavelength-specific polarizers, Glan Laser models operate effectively across a wide spectral range, simplifying system design and reducing the need for multiple components in multi-wavelength applications.
These polarizers are also highly stable in sensitive optical setups, as the air-spaced structure minimizes internal reflections and scattered light. This stability is crucial in high-precision applications, such as laser metrology, spectroscopy, and alignment systems, where maintaining beam integrity is paramount. Additionally, the robust construction of Glan Laser Polarizers extends component lifespan, providing reliable, long-term performance.
Optimal Applications: Glan Laser Polarizers excel in high-stakes scenarios where polarization integrity must be preserved, including:
- Industrial laser systems: High-power laser cutting and laser welding where both endurance and polarization purity are required.
- Scientific instrumentation: Systems such as spectrometers and interferometers, where signal interference must be minimized.
- Defense and military: Environments that require components resistant to thermal and mechanical stresses.
These attributes make Glan Laser Polarizers critical in applications where typical polarizers cannot meet performance demands, enabling superior control in industrial, scientific, and defense-related optical systems.
6. Installation and Handling of Glan-Laser Polarizers
Proper integration and handling of Glan Laser Polarizers are essential for maintaining performance and ensuring durability in high-energy optical systems. When installing, align the polarizer carefully to match the polarization axis of the incoming light. Misalignment can lead to reduced extinction ratios and compromised beam quality. Use compatible mounts that support the polarizer securely without applying excessive pressure, which could damage the delicate calcite crystals or air gap.
During operation, keep the polarizer clean and free from dust and contaminants. Contaminants on optical surfaces can cause scattering or absorption, degrading performance, particularly in high-power applications. Use compressed air to remove particles and a soft, lint-free cloth with optical-grade cleaning solution to gently clean the surfaces, avoiding any abrasive materials.
6.1. Common Challenges and Troubleshooting Tips
- Beam Deviation: If you observe unexpected beam deviation, check that the polarizer is properly aligned with the incoming light. Small adjustments may be required to optimize alignment.
- Thermal Stress: In high-power applications, thermal buildup can be a concern. Ensure adequate cooling in the surrounding system to prevent temperature-induced stress on the polarizer.
- Reduced Extinction Ratio: Contamination or misalignment can lower the extinction ratio. Cleaning the surfaces and verifying alignment often resolve this issue.
- Surface Damage: Avoid touching the optical faces directly, as oils from skin can damage the polished surface and impact performance. Handle the polarizer by its edges or mount.
Following these guidelines helps maintain the polarizer’s high extinction ratio and extends its operational life, ensuring stable performance in demanding optical setups.
7. Conclusion
Glan Laser Polarizers are indispensable components in high-power and precision optical systems, offering unparalleled polarization purity, durability, and broad wavelength compatibility. Their air-spaced design minimizes thermal stress and enables high damage thresholds, distinguishing them from other polarizing technologies. We have covered the fundamental principles, performance characteristics, types, and practical handling considerations of these polarizers, as well as the unique advantages they bring to demanding applications.
In advanced fields such as laser metrology, spectroscopy, and high-power industrial applications, Glan Laser Polarizers enable precise control and stability, supporting the development of cutting-edge optical technologies. Their role in ensuring consistent, reliable performance under extreme conditions makes them essential for optical engineers aiming to push the boundaries of laser and photonics systems. Glan Laser Polarizers will continue to be a vital tool in the advancement of high-stakes optical technologies.
Did you know, that we have a dedicated product category for Glan-Laser Polarizers? if you are in the market, check that out first.
