LeviPrint technology, short for levitation printing technology, is a touch free manufacturing system currently in development. The technology is being developed with a few new contributions being researched in 2022. The Association for Computing Machinery released a paper which shows many of the new contributions showcased at SIGGRAPH ‘22. In this article we will discuss how LeviPrint technology works and its potential.

Structure created with spherical particles published by UPNA/NUP- public University of Navarre. Courtesy of EandT.com
Introduction to LeviPrint: a novel 3D manufacturing technology
Utilizing a set of optimum acoustic fields, a LeviPrint apparatus can suspend and dynamically manipulate elongated objects such as sticks, beads, or droplets. Researchers are creating new optimal methods of using these acoustic fields. The hope is that novel fabrication techniques will be developed soon with this technology. Recent contributions have been collected and summarized at a SIGGRAPH ‘22 conference. For a more in depth look at the SIGGRAPH ‘22 conference proceedings please refer to this research paper pdf for your personal use.
The trapping of a bead using ultrasonic waves is not new. LeviPrint researchers capitalize on this and document how to manipulate and trap elongated objects. This ability to trap and move sticks or elongated objects offers a new contactless manufacturing potential.
Researchers and engineers are currently taking the next steps in making this innovation a reality. In a research paper released after SIGGRAPH 22’ conference, researchers propose the idea of using a LeviPrint levitator as an end effector.
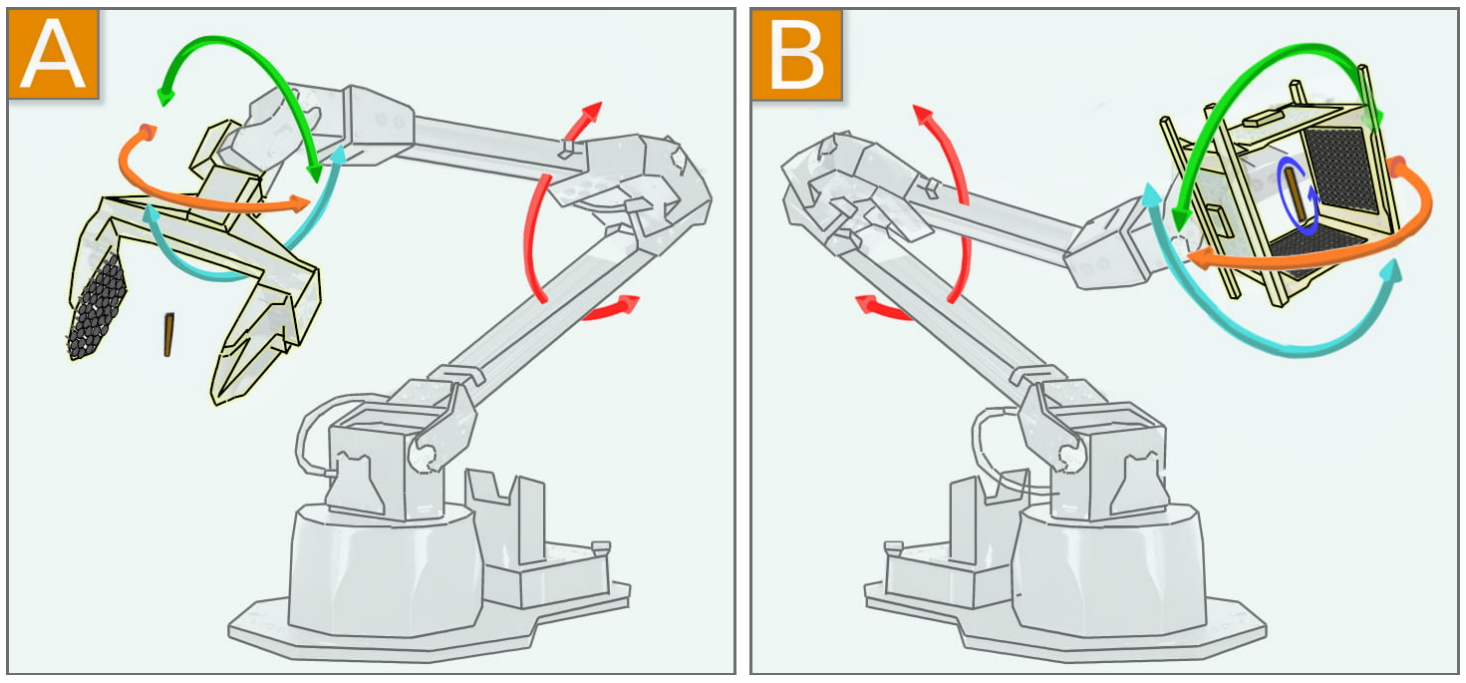
A proposed idea for using a levitator as an end effector. A) using a fixed single axis levitator with bowl geometry. B) using 4 orthogonal flat arrays in cube structure. Courtesy of UPNA/NUP-Public University of Navarre
How LeviPrint Technology Works
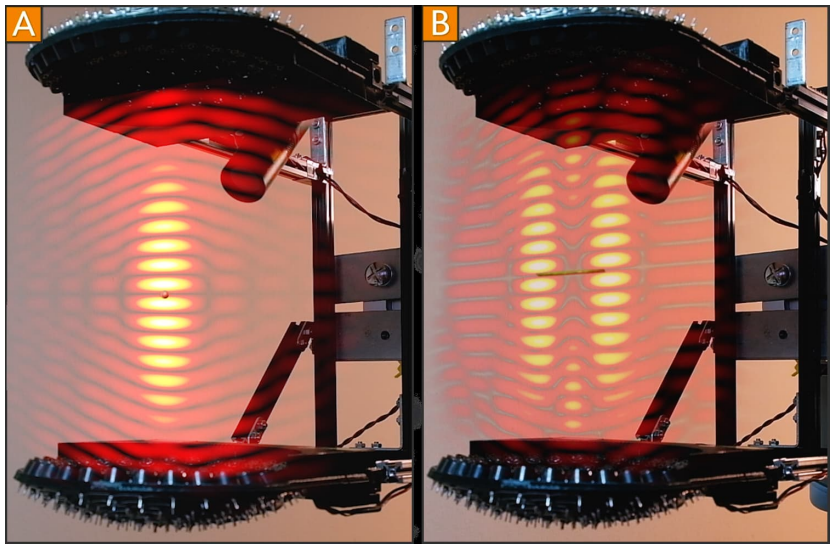
A bead (A) and a stick (B) levitated using single-axis acoustic arrays. Image courtesy of UPNA/NUP-Public University of Navarre
As mentioned before, LeviPrint technology uses acoustic fields to trap objects within them. A levitator, which is an array of acoustic emitters, produces ultrasonic waves. The ultrasonic waves exert a pressure on the levitated object which keeps the object afloat. Researchers have a model using Gor’Kov potential to determine the needed amplitude and frequency of the emitters. The image above exemplifies how acoustic fields surround a stick or bead. These ultrasonic levitators have the capacity to create “traps” around a desired object which holds the object in place. Note how the stick has 2 congregations of light intensity along the ends. These two points are where the stick is “trapped” in order to constrain it whilst midair. Many methods to do precisely this were tested. This includes trapping at center, trapping at sides, minimizing Gor’Kov potential, and minimizing a weighted Gor’Kov potential.
How LeviPrint uses Acoustic Manipulation
An ultrasonic wave is generated using acoustic emitters. The acoustic field generated is then dynamically modified through precise adjustment of the emitters’ phase and frequency. Researchers found that using a standing wave using 2+ emitter arrays produces 8 times the trapping force of one array. The interesting and novel capability to make note of is the control of the orientation of elongated objects. Using this control, more complex constructions begin to be feasible. An impressive example is that of a cube as seen below mid construction.
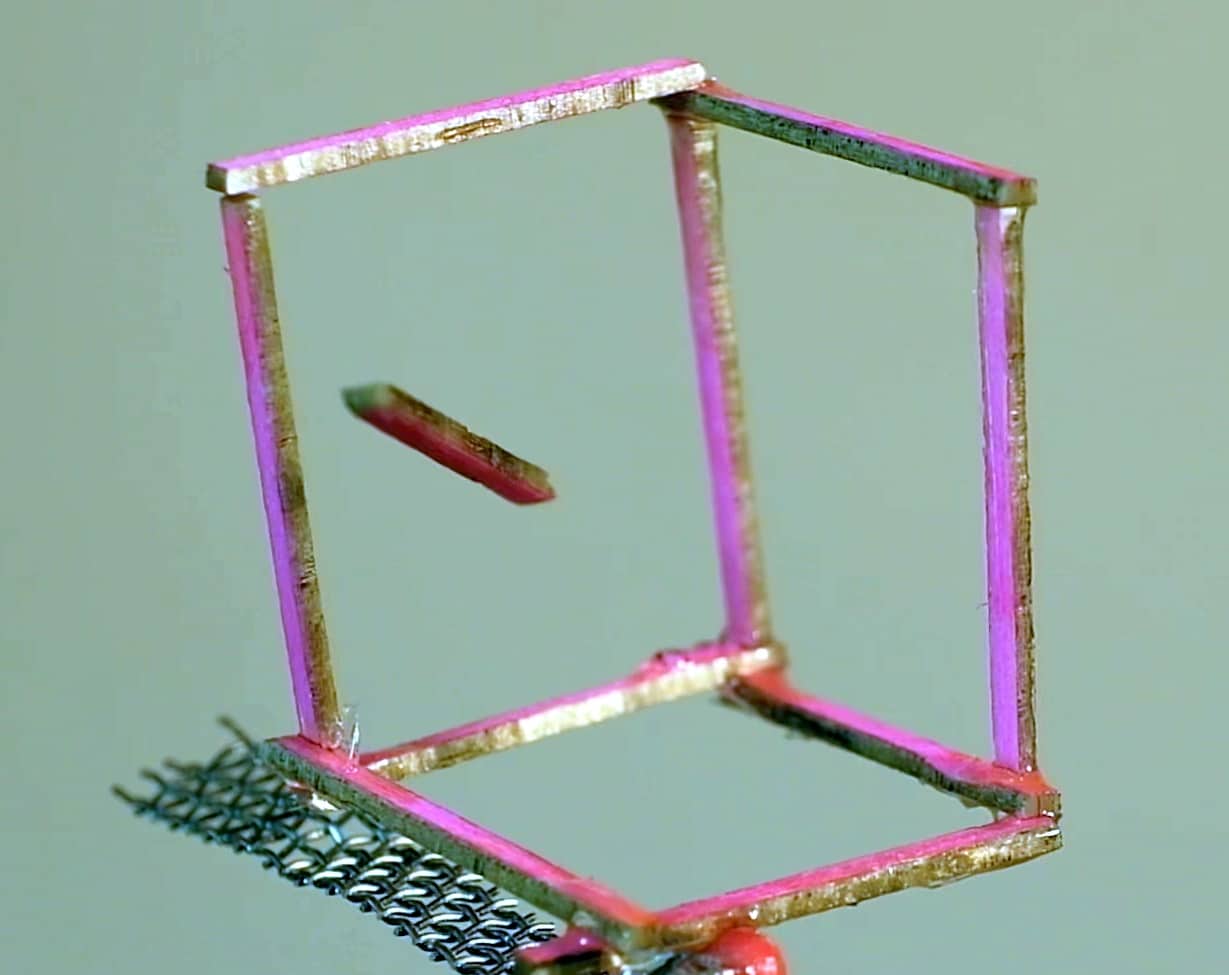
Scientists use sound array to build cube from 12 levitating segments. Image courtesy of CourthouseNews.com
Fabrication using LeviPrint Technology
The touchless nature of this technology has potential to become a fundamental tool in contactless processing. By combining primitive building techniques with beads, sticks, and droplets, more complex fabrications suddenly become possible. It should be noted that many of these operations can be done independently (i.e. multiple beads can be levitated and moved independent of one another). One method described by researchers is using the levitator to hold sticks together and then levitating glue to the joint.
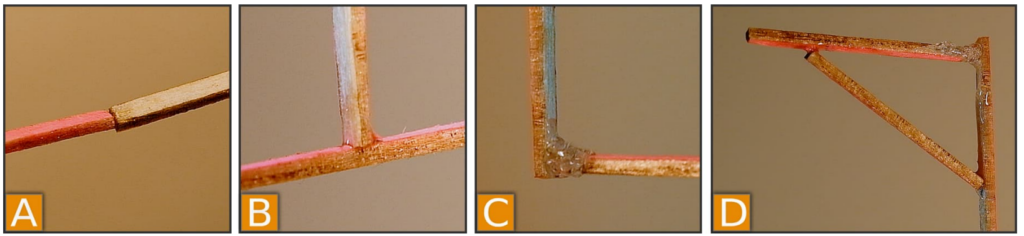
These are types of joints able to be made with LeviPrint A) Butt joint. B) L-joint. C) T-joint. D) Mitted joint. Image courtesy of UPNA/NUP-Public University of Navarre
The researchers have documentation of working with the following:
- Particles, beads, and glue in contact with one another.
- UV resin, using the same techniques used for particles. Carried resin cures once reaching its target position.
- Complex objects, using previously shown joints and methods more complex objects could be made. Notably a cube and bridge as shown below.
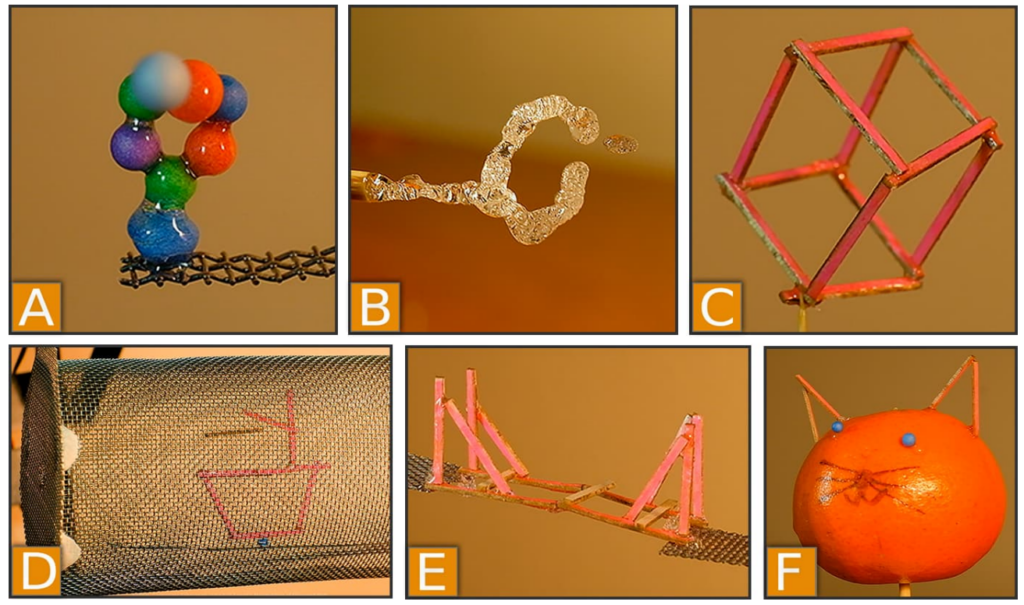
Items fabricated by researchers. A) Particles joined by glue in a loop. B) Glue droplets cured in a loop. C) A cube made with L-joints. D) A stick construction levitated inside a container. E) Bridge construction made of levitated sticks. F) Construction working around solid object. Image courtesy of UPNA/NUP-Public University of Navarre
LeviPrint technology compared to other fabrication methods
Due to the new nature of this technology it is apparent that other fabrication methods are currently superior. However, one notable advantage that LeviPrint has is the ability to manipulate objects without direct contact. The previous section showed a construction done within a cylinder (See image D) above). This construction would be entirely impossible using other means such as 3D printing. For a better look at 3D printing please refer to our introductory guide. LeviPrint has the ability to have obstructions between the manipulated object and the manipulator. Due to this novel ability LeviPrint may become an important tool for biomedical constructions. Now, consider the possible applications as a non-intrusive method of accessing constructions within the human body.
Another notable comparison would be the material variety available for the method. Many individual 3D printers limit material usage to just plastics or a single type of material per machine. Whereas LeviPrint already has the capability to use very different materials (resin and sticks) simultaneously.
When compared to optical trapping, acoustic manipulation has a larger ratio of input power to radiation force. Additionally, the trapping is non-damaging in acoustic manipulation used by LeviPrint.
Conclusion
LeviPrint is a new and potential filled technology for contactless assembly and fabrication. Current researchers work while hoping more advanced techniques begin development alongside them. Additionally, the proposed idea for using levitator arrays is one that holds promise for a touchless assembly line. As the technology improves so too will techniques for using it in novel and innovative ways.
Relating Reading
At the end we included some further reading materials that will help you better get acquainted with this new fabrication technology:
SIGGRAPG 22’ conference: “LeviPrint: Contactless Fabrication using Full Acoustic Trapping of Elongated Parts.” This is the original paper published by the scientists from Spain, UK and Brazil, on which we have based this blog article.
EandT article: “LeviPrint: Contactless Fabrication using Full Acoustic Trapping of Elongated Parts.” A relatively new article that discusses the practical setup used for this novel technology.
Gadgetany article: “LeviPrint Enables Contactless Building Construction Using Levitation Technique” Yet another article showcasing some examples of where this new fabrication technology can become useful.
Did you like this blog post? If you did, please subscribe and share on social media.
