Hunting. What was a pursuit once necessary for survival is now a sporting pastime for those in the developed world. Many of the animals are nocturnal which makes the night time a preferred time for hunting. Unfortunately (for the hunters), nightfall shifts the odds into the animals’ favor. Night vision optics can help take some of the power back into the hands of the hunter. Having night vision capabilities while hunting is important for several reasons. Shooting accurately — whether one is a casual, recreational hunter or a trophy hunter — is critical. Firstly, it can help make proper identification of an animal easier. It also allows for better targeting of the proper body part of the animal to take it down most effectively while maximizing the yield and minimizing waste.
Today’s post is sponsored by DataRay Inc. – expanding the frontier in technologies for laser beam analysis
Another important factor is that missing a target can quickly turn careful days of stalking into a fruitless effort. Thankfully, night vision optics makes both the identification, hunt, and shot itself a lot more precise. There are numerous options available whether you are hunting with a firearm or a bow.
Two Types of Night Vision Optics
While better gear does not guarantee a better hunter, it can certainly help. Having a proper understanding of the gear and how to use it properly is as important as the use of high quality optics themselves. Older generations of night vision use an image intensifier tube. Visible and infrared light would be collected though the objective and sent through the intensifier tube. The image intensifier tube is effectively a photocathode and a vacuum tube called a microchannel plate. The photocathode’s purpose would be to convert the light into electrons and then the microchannel plate amplifies the electric signal. These electrons would then collide with a phosphor-coated screen to create the green, glowing images associated with night vision. Unfortunately, using these kinds of night vision devices during the day causes damage to the intensifier tube due to high influx of energy exceeding the damage threshold.
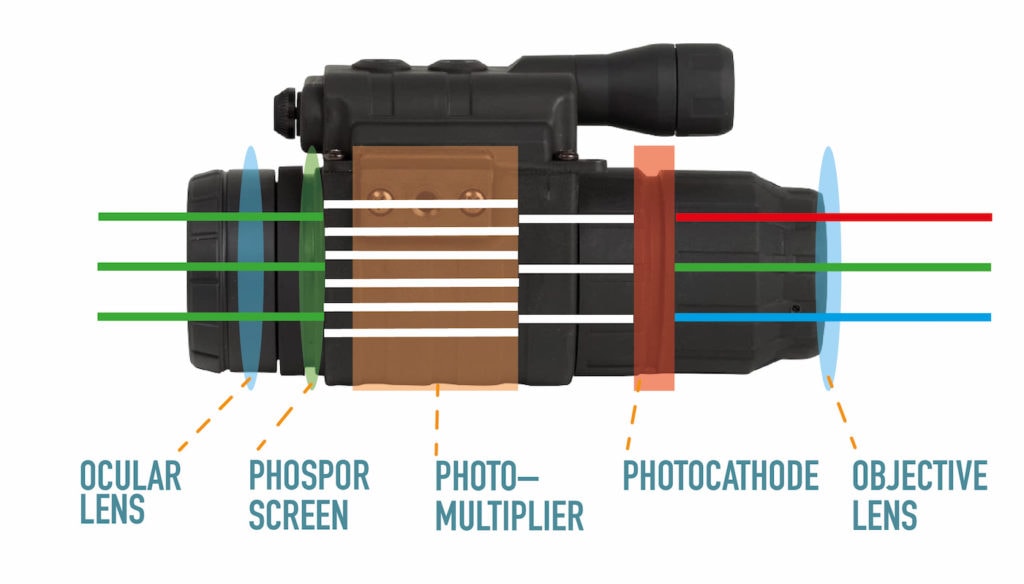
Diagram describing the basic design of a night vision scope. Courtesy of OpticsMag.
Digital night vision works by taking the system’s incoming light and converting it to a digital signal through a CMOS sensor. The digital image relayed by the sensor is then magnified and displayed on an LCD screen. Depending on the size of the CMOS sensor, better resolution of the imaged scene can be achieved. Most digital night vision devices are able to be used both during the day and the night.
Hunting with Night Vision
Night vision binoculars and night vision riflescopes are two of the most common ways of integrating night vision capabilities into one’s arsenal. Getting a pair of night vision binoculars for spotting is a good start. When hunting, it is always important to be aware of one’s surroundings. Surveying the area for an animal and the surrounding area with a spotting scope or binoculars is often referred to as “glassing”. It is imperative to know what lies beyond and behind one’s prospective target. Binoculars are useful for glassing whereas a riflescope is good for the act of shooting itself. A night vision riflescope makes taking a shot at night not only more precise, but possible.
There are different factors to be considered when in the market for a good night vision scope or binoculars. Durability and battery life are important since one may be trekking through rugged terrain with limited opportunities to recharge an optical device. Magnification, accuracy, and sensitivity to elements (such as heat, cold, humidity, and pressure) are also things to be considered when purchasing an optic. The field of view and eye relief need to be reviewed, too. Eye relief is especially important for a riflescope since one’s reaction to a firearm’s recoil can affect the shot.
Another option besides night vison scopes or binoculars is to use a night vision camera. Sionyx, for instance, is a company that focuses specifically on night vision cameras. While these night vision cameras are not designed solely for hunting purposes (think law enforcement or surveillance as well) they can be paired with a riflescope or magnifier. These cameras employ digital night vision technology. CMOS sensors of such cameras detect into the near infrared range, allowing it to have better nighttime performance. Their CMOS sensor design allows the cameras to be used equally well during the daytime as during the night. Some of those cameras boast solid performance even in conditions where the ambient lighting is as low as 2 millilux. For reference, the illumination provided by moonlight (depending on the phase of the moon) roughly tends to be around 100 millilux.
Hunting Using Infrared Optics
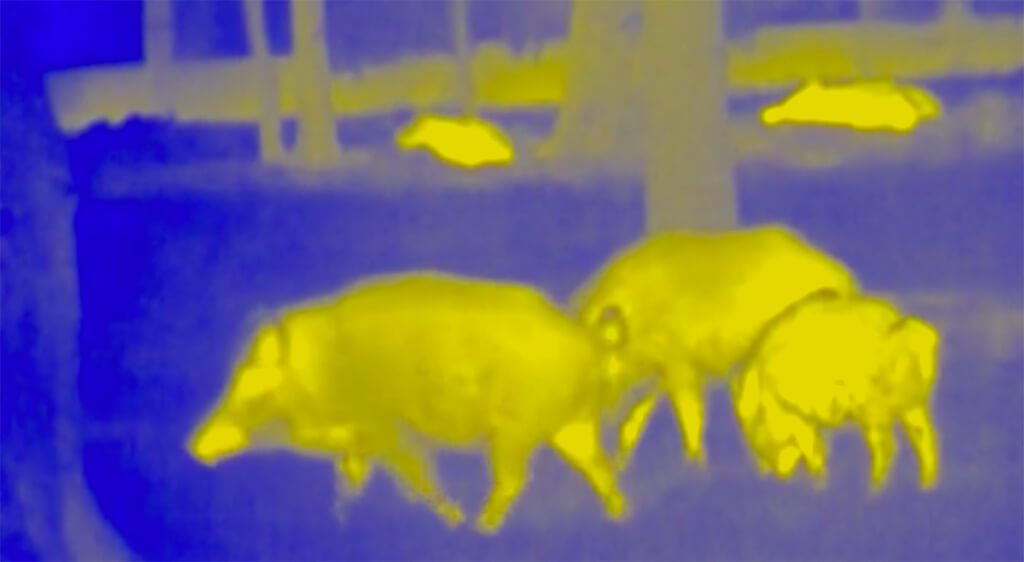

An image of hogs obtained using infrared optics. Courtesy of Sionyx.
There is some discussion between using thermal optics or night vision during a hunt. Thermal imaging technology tends to have a lower resolution than both analog or digital night vision systems. With thermal imaging, there could also be a bush or other foliage in front of an animal blocking one’s shot but in very low light and using thermal imaging, one would be unable to tell since only the animal would be giving off a heat signature. However, this could also be seen as advantageous, since with night vision it would be difficult to determine if there was anything beyond the bush or foliage. In the case of infrared optics, one would know there was an animal present whether something was blocking it (given that “something” was not a hard barrier).
Thermal optics are also preferred over night vision in foggy or smoky conditions which would not affect infrared performance. This type of optic is not reliant on ambient light since it detects the heat signatures of living creatures. A downside of thermal imaging is that it is rendered nonfunctional in extremely cold conditions. Most hunters seem to agree that infrared imaging is generally preferable to night vision, though night vision is far superior when identifying game.
Are you a hunter? What’s your favorite tool for night vision? Comment below.
