Ever since the introduction of man-made plastics in 1862 humanity has curated various methods of making plastic parts. Very similar to metals, plastics are everywhere in our world. Due to the rapid rate and low cost at which plastics can produce parts, plastics feature often in prototypes and other parts which do not require the strength of metals. In this post we will give a brief introduction of many common plastic part manufacturing processes.
Plastic Part Manufacturing Processes
When it comes to manufacturing parts with plastic it is important to know that two main categories of plastics exist: Thermoplastics and thermoset plastics. The main difference between thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics is that thermoplastics can go through numerous melt/solidification processes while thermosetting plastics cannot melt without mostly decomposing.
Plastics have their own sets of material properties which require different manufacturing processes as we discuss below:
Extrusion
Extrusion is the process by which melted plastic is pushed through a die. The shape of the die is then a cross section of the extruded plastic. After the molten plastic exits the extruder it cools into the desired shape. This process is seen often in 3D printers which have an extruder on rails.

The extrusion process visualization. The screw will push melted plastic through the die to create a variety of shapes depending on the die shape and extruder movement. Image courtesy of Pri-Plastics.com
3D Printing
3D Printing is the process where layers (a.k.a. cross sections) of a 3D model are printed on top of each other. The process often uses an extruder but mostly for thermoplastics. This process works using FDM (Fused deposition modeling), SLA (Stereolithography), or SLS (Selective laser sintering) among other printing methods. This method is the most popular for prototyping due to very low startup costs. 3D printing is very popular for low volume quantities of complex parts. Processes for both thermoset plastics and thermoplastics exist. For a more in depth introduction to personal 3D printing, visit our post about the basics!
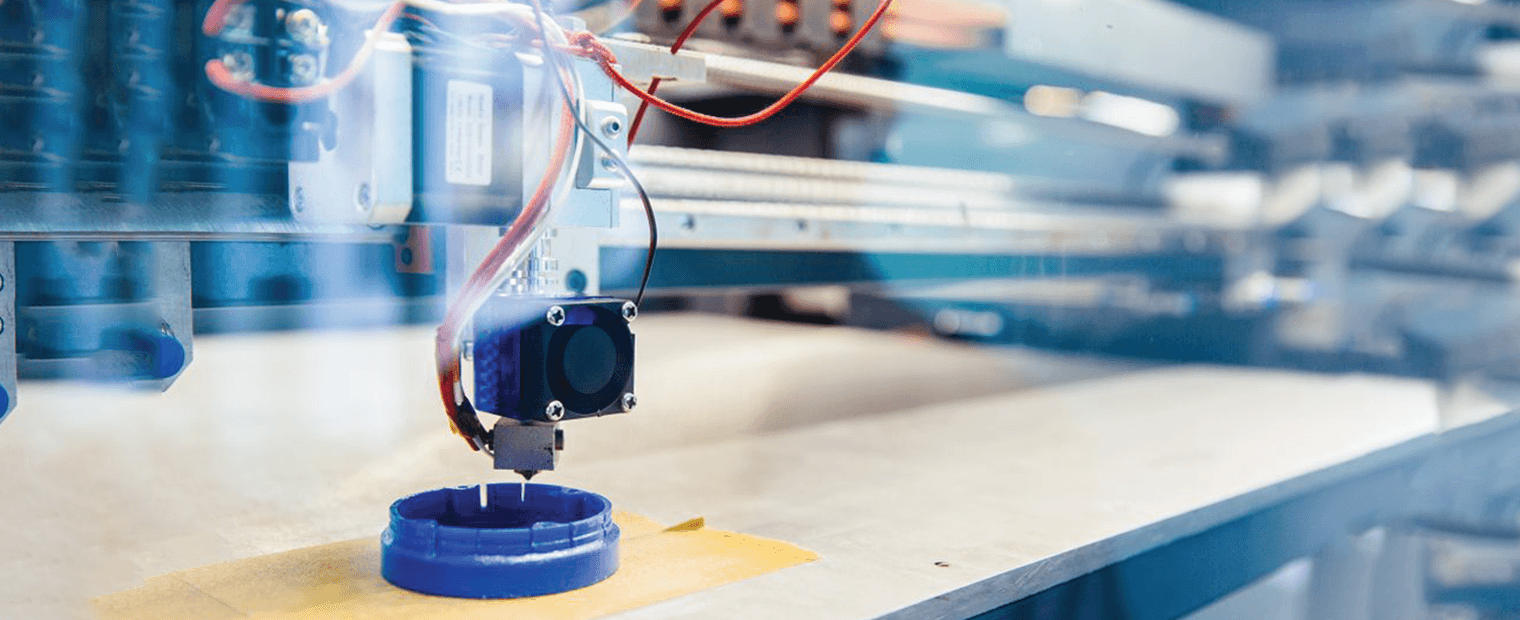

3D printing using an extruder to print a part on a work surface. image courtesy of ubqmaterials.com
CNC Machining
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process which includes milling, lathing, and drilling. This process begins with a solid piece of plastic which then receives shaping done by a tool. In most cases there is an element of rotation, such as a spinning drill bit or rotating the piece along an axis while carving with a fixed tool (such as a lathe). This process is most common for producing holes in parts of plastic as shown below.
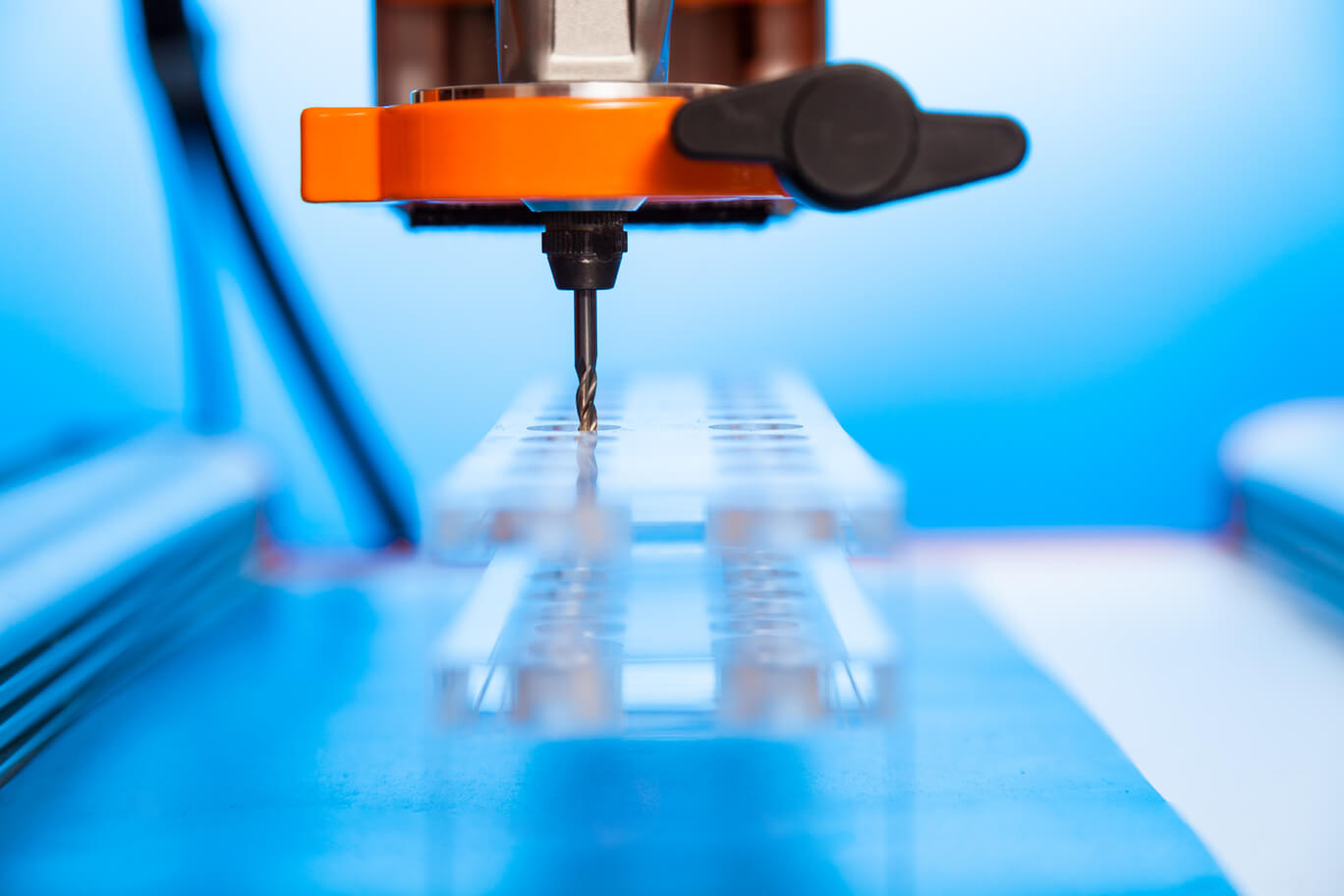
Machining on plastic using a drill bit mounted to a precise arm. image courtesy of 3erp.com
Polymer Casting
Polymer casting is the process where a liquid form of a polymer like a resin or rubber fills a mold where it then solidifies. After being cast normally there is a little more processing to be done before the part is ready. However, due to the chemical nature of this process, molds are often not reusable indefinitely. The detail of the resulting parts makes this process popular for use in making plastic statues and complex volume components.

Concept diagram for polymer casting, which has reactive elements in a mold. Image courtesy of polymerplastics.com
Rotational Molding
Rotational molding (aka rotomolding) is the process where powdered thermoplastic is heated in a hollow mold. The heated thermoplastic then spins along 2 axes which allows the creation of hollow objects. This process is also available for thermosets while being less common in rotational molding. The ability of this process to produce hollow parts such as hollowed statues has popularized rotomolding in use for containers that hold fluids.

Rotational molding as demonstrated by 4 steps. Image courtesy of bpf.co.uk
Blow Molding
Blow molding is the process which results in hollow pieces of plastic. This process works by inflating hot plastic inside of a mold in order to form it. This process is most popular in creating a large quantity of hollow plastic parts. Blow molding is very common for use in making drinking bottles.
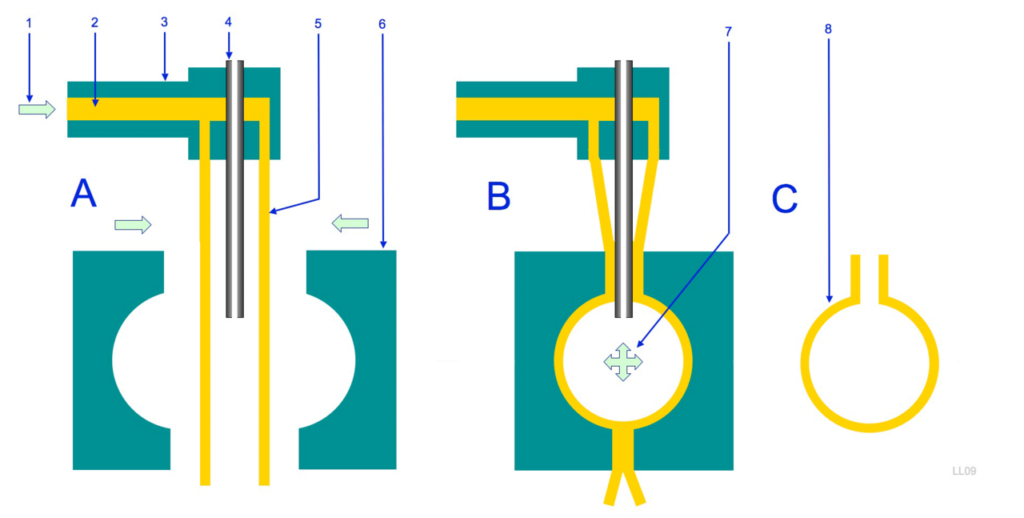
Blow Molding Process Explained: From Extruder to Final Product – A detailed diagram showcasing the sequential stages and key components involved in the blow molding technique, with bilingual labels in English and Dutch for inclusive understanding. Image courtesy of Laurensvan Lieshout
Vacuum Forming
Vacuum forming, also known as thermoforming, is a process where plastic is heated and then formed using a mold. Due to the variation in tool cost for this process, the price for this process can be very cheap or very expensive. This is because molds created from wood, other plastics (including 3D prints), and metal are viable. The variety in mold prices consequently means a variety in startup costs. This heated process uses thermoplastics more often than thermoset plastics. Common plastic food containers often come from a vacuum forming process.
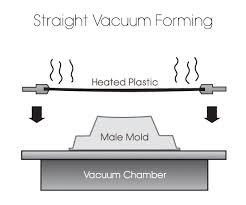
This is the concept of vacuum forming of a straight sheet of plastic. Image courtesy of emcoplastics.com
Injection Molding
Injection molding is the process by which molten thermoplastic is pushed into a mold. Mass production is the specialty of this plastic manufacturing process. The main benefit is that it is very easy to produce many custom injection molded parts, quickly and with high fidelity. Due to having high startup costs, manufacturing large quantities of a product makes this method viable. For example: plastic lids, bottles, toys, or plastic kitchen utensils.
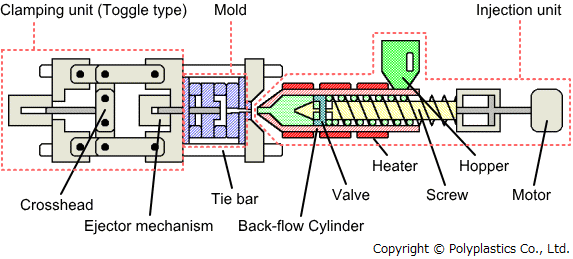
Injection molding pushes melted plastic into a mold using a heated screw design which pushes the plastic when turned. Image courtesy of polyplastics.com
Conclusion
In this blog post we introduced several plastic manufacturing processes which represent only a subset of all the processes in use today. Material selection and the end use play a large role in selecting the appropriate process. Nonetheless, the versatility of these processes make certain plastic parts conducive to making them with interchangeable processes, sacrificing and gaining effects on its production. Sometimes it is the quantity of product that is the biggest determiner of which process to choose. It only seems logical that quantity matters when we consider the scope of how many plastic products circulate in the industry and home. Hopefully this brief list of plastic manufacturing processes leaves you more informed on the plethora of processes that exist out there to make the products you use everyday.

Good article – I was filming at a plastic bottle manufacturing facility just a few weeks ago hence the reading. Luke.
Thank you, Luke!
Great overview of the main plastic manufacturing methods—especially the inclusion of 3D printing alongside traditional processes like extrusion and molding. I’m particularly interested in <a href="https://www.welchplastics.com/">custom plastic manufacturing</a>, where combining methods (like a printed preform plus overmolding) could unlock both design flexibility and precision. Love how the guide lays out the building blocks for anyone exploring tailored plastic solutions!