Description
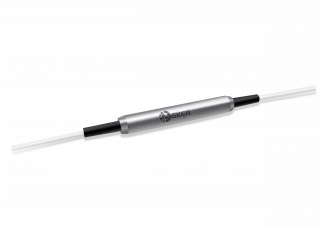
The GKER Photonics GK-WDM Series Wavelength Division Multiplexers (WDMs) are designed to efficiently combine or separate light at different wavelengths. Operating across the 635 nm and 1064 nm wavelength bands, these multiplexers excel in performance with exceptionally low insertion loss and minimal polarization dependence. The components are engineered for high isolation and excellent environmental stability, making them highly reliable for demanding applications.
These WDMs are ideal for use in laser marking systems and fiber optics instrumentation, where precise wavelength management and signal integrity are crucial. With features like high isolation, low thermal sensitivity, and robust optical power handling, the GK-WDM Series ensures consistent performance across a wide temperature range. The multiplexers are built to withstand various environmental conditions and mechanical stresses, ensuring longevity and reliability in various applications.
635 -1064 nm Wavelength Division Multiplexers-WDM
Specifications
| Operating Wavelength: | 1064 nm |
|---|---|
| Operating Bandwidth: | Not Specified |
| Isolation (min): | 10 dB |
| Max Power Handling: | 5 W |
| Polarization Maintaining: | No |
| Longer Operating Wavelength: | 1064 ± 5 nm |
| Max. Insertion Loss: | 0.2 dB |
| Max. Polarization Dependent Loss: | 0.1 dB |
| Min. Isolation: | 20 dB |
| Shorter Operating Wavelength: | 635 ± 5 nm |
| Max. Insertion Loss: | 1.0 dB |
| Min. Isolation: | 10 dB |
| Thermal Stability: | ≤ 0.002 dB/℃ |
| Min. Return Loss: | 55 dB |
| Min. Directivity: | 55 dB |
| Max. Optical Power (Continuous Wave): | 5 W |
| Operating Temperature: | - 40 to + 75 ℃ |
| Storage Temperature: | - 40 to + 85 ℃ |
Features
- Low Insertion Loss: Maximizes signal transmission with a maximum loss of 0.2 dB for 1064 nm and 1.0 dB for 635 nm
- Minimal Polarization Dependent Loss: Ensures stable performance with a maximum PDL of 0.1 dB
- High Isolation: Provides a minimum isolation of 20 dB, reducing signal interference between channels
- Excellent Thermal Stability: Maintains performance with a thermal stability of ≤ 0.002 dB/°C
- High Return Loss: Guarantees a minimum return loss of 55 dB, ensuring minimal signal reflection
- Robust Optical Power Handling: Supports up to 5 W of continuous wave optical power
- Wide Temperature Range: Operates reliably in temperatures from -40°C to +75°C, with a storage range of -40°C to +85°C
Applications
- Laser Marking Systems: Ideal for precise wavelength management in industrial laser marking applications
- Fiber Optics Instrumentation: Utilized in various fiber optic instruments requiring accurate wavelength division and minimal signal loss
- High-Power Optical Systems: Suitable for environments with high optical power requirements and demanding performance standards
Frequently Asked Questions
What wavelengths does this WDM support?
What is the typical insertion loss for this WDM?
What is the maximum polarization dependent loss?
What is the minimum isolation provided by this WDM?
What is the thermal stability of this WDM?
What is the maximum optical power it can handle?
What is the minimum return loss for this WDM?
What is the operating temperature range?
What is the storage temperature range?
What fiber types are compatible with this WDM?
Similar Products





Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle
