Introduction
Laser-cutting machines are an invaluable asset in a multitude of industries, from artisanal small businesses to large-scale manufacturing facilities. The integration of multiple laser material processing machines into a machine network, however, can present its unique set of challenges, especially when it comes to managing jobs and file sharing across devices. The solution? Harnessing the power of Ethernet connectivity.
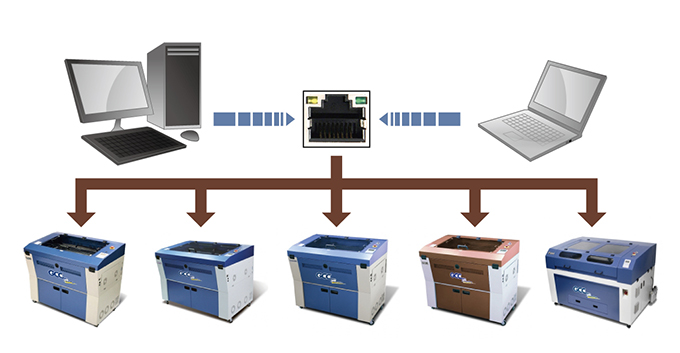
Ethernet connectivity enables the linking of multiple laser-cutting machines into a cohesive network, providing the ability to share files seamlessly and coordinate tasks to maximize productivity.
In this guide, we will delve into a step-by-step process of connecting various laser-cutting machines into a single, unified network. We’ll cover all the necessary bases, including:
- Hardware Requirements: The essential physical components to get your network up and running
- Software Requirements: The crucial programs to streamline your operations
- Network Setup and Machine Configuration: Detailed instructions to connect and configure each machine to the network
- File Sharing and Job Management: How to efficiently manage your projects across the network
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Dealing with common issues that may arise and maintenance practices to keep your network running smoothly
By the end of this guide, you will have gained an in-depth understanding of how to efficiently set up and manage a network of laser cutters utilizing Ethernet connectivity. So, whether you’re an industry veteran looking to optimize operations or a novice eager to enhance your workflow, this guide has got you covered.
1. Hardware Requirements
When considering the integration of multiple laser cutting machines via Ethernet connectivity, several hardware components become indispensable. These key components include:
- Router or Switch: This is the heart of your network. It manages traffic between your machines and helps to connect them to other networks or the internet if needed.
- Ethernet Cables: These are the lifelines that physically link your machines to the router or switch. They transmit data between your laser cutters and enable them to communicate with one another.
- Network Interface Card (NIC): Each machine requires an NIC. This device allows your laser cutter to interface with the network by translating the data from the machine into a format that can be transmitted over the network.
While assembling these hardware components, remember that the scale of your business, the number of machines you wish to integrate, and your budget are all pivotal factors influencing your selection.
A Local Area Network (LAN) is most commonly utilized for connecting laser cutting machines, given its capability to support multiple devices in a relatively confined area. However, depending on your unique business requirements, you may opt for a Wide Area Network (WAN) or even a Virtual Private Network (VPN). Installing a VPN app across multiple devices can provide an additional layer of security and privacy, ensuring secure communication for networked laser cutting machines.
It’s advisable to invest in reliable, high-quality hardware from reputable brands to ensure consistent and stable performance. Doing so will optimize your operations, reduce potential downtime, and ultimately, enhance the efficiency of your networked laser cutting machines.
2. Software Requirements
To successfully run a network of laser cutting machines, there are several software requirements beyond the specific cutting software for each device. These additional components include network management software, firewall software, and file-sharing software.
- Network Management Software: This software aids in monitoring network traffic and maintaining optimal network performance. It can help detect and promptly resolve network connectivity issues. Popular options include Cisco Prime Infrastructure, SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, and Nagios XI.
- Firewall Software: This software is crucial to safeguard your network from unauthorized access and various security threats. It can prevent malicious traffic from penetrating your network and can restrict access to certain websites or applications. Renowned firewall software options include Norton Internet Security, McAfee Firewall, and ZoneAlarm.
- File-Sharing Software: File-sharing software is essential for exchanging design files and job information between laser-cutting machines. This facilitates multiple machines to work simultaneously on the same project, thereby enhancing productivity and efficiency.
Step-by-step Setup Process for the Software
Here are detailed steps to set up the required software for managing multiple laser cutters using Ethernet connectivity:
- Choose Suitable Software: Select network management, firewall, and file-sharing software that is compatible with your laser cutters and satisfies your operational requirements.
- Install the Software: Install the software on a computer that will serve as the central server for the laser cutters. Ensure this computer meets the system requirements of the chosen software.
- Configure Network Management Software: Set up the network management software to oversee the network traffic of the laser cutters. This will enable the early detection of issues such as dropped connections or sluggish speeds.
- Configure Firewall Software: Arrange the firewall software to shield your network from unauthorized access. This includes setting rules for inbound and outbound traffic and establishing VPN connections for remote access.
- Configure File-Sharing Software: Set up the file-sharing software to enable laser cutters to exchange design files and job information. Ensure compatibility with the laser cutters and correct file permissions.
- Connect Laser Cutters to the Network: Connect the laser cutters to the network using Ethernet cables. Set their network settings to ensure connection to the correct network and unique IP addresses.
- Test Connectivity: Verify the connectivity between the laser cutters and the network by sending a test job to each cutter and observing its progress.
- Troubleshoot Connectivity Issues: Address any connectivity issues promptly. Troubleshooting can involve checking network settings, rebooting the laser cutters or the server, and resetting network devices. It’s beneficial to maintain detailed records of troubleshooting steps to streamline future issue resolution.
3. Network Setup and Machine Configuration
Creating a network of laser cutting machines involves a three-pronged approach: the physical installation of hardware components, network configuration, and security setup. It’s imperative to meticulously plan the network setup and ensure each machine is assigned a unique IP address. Network configuration involves tailoring the settings of the router or switch and establishing network protocols, while security setup pertains to configuring firewalls and ensuring network access is limited to authorized personnel only. With the right tools and knowledge, common network setup issues such as IP conflicts, connectivity issues, and firewall configuration can be addressed promptly and efficiently.
Step-by-step Setup Process
Follow these steps to set up your network and configure each machine:
- Physical Connection: Connect each laser cutter to the network using Ethernet cables.
- Accessing Network Settings: Power on each laser cutter and navigate to the network settings in the device menu.
- Assign IP Addresses: Assign a unique IP address to each laser cutter within the same subnet as the network. Ensure each IP address is different to avoid any conflicts.
- Configure Subnet Mask and Default Gateway: Configure the subnet mask and default gateway in the network settings for each laser cutter. These should be identical for all devices on the network.
- Test Connectivity: Test the connectivity between each laser cutter and the network using a ‘ping’ command for each IP address.
- Test Connection to Computer: If the connection is successful for each laser cutter, test the connection to a computer on the network. This can be done by opening the computer’s web browser and entering each laser cutter’s IP address into the address bar.
- Verify Successful Connection: If the connection to each laser cutter is successful, your machines are now ready for networked operation.
Please note, the specific steps can vary depending on the make and model of the laser cutter, as well as the details of your network setup. Always refer to the device and network manuals for instructions specific to your situation.
4. File Sharing and Job Management
Laser cutting operations significantly benefit from the efficient sharing and management of design files and job information. When working with a network of multiple laser cutters, a centralized system is vital. Using a file server or cloud-based storage solution serves as a common repository for all design files and job data, simplifying file sharing and ensuring every machine has access to the latest designs.
Laser cutting files are able to be shared with a Samba file server.
Additionally, incorporating job scheduling software into your operations optimizes laser-cutting jobs’ management. It fosters efficient job processing, thereby minimizing the risk of errors or delays.
When selecting file sharing and job management software, compatibility with your network setup and the features you require should be top considerations. Numerous open-source solutions like Samba, ownCloud, and Nextcloud offer customization and scalability. For larger-scale operations demanding advanced features such as version control, access permissions, and audit trails, enterprise-level solutions like Microsoft SharePoint and Dropbox are excellent choices.
As you set up a file server or cloud-based storage solution, factor in the storage requirement for all design files and job data and the frequency of access. High-resolution design files may rapidly consume a substantial amount of storage. As such, consider incorporating storage management practices such as archiving or compression to optimize your storage usage.
5. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Network connectivity and software integrity are vital for optimal performance of a network of laser-cutting machines. Regular maintenance checks and timely software updates can prevent costly downtime and ensure smooth operations. It’s also crucial to keep a record of maintenance tasks and troubleshooting steps to quickly identify and resolve any future issues.
When network or software issues arise, it’s essential to troubleshoot them promptly to minimize downtime. Common issues can include network connection errors, software malfunctions, and even security breaches. Troubleshooting involves isolating the issue to determine whether it’s related to the network, software, or machine hardware. Once the issue is identified, solutions might include resetting the network, updating or reinstalling software, or addressing hardware faults.
Here are some practical guidelines on how to maintain your laser cutter network and software effectively:
- Regular Network Monitoring: Regularly monitor network traffic to detect any anomalies that might indicate potential issues. Use network monitoring software tools to streamline this process.
- Software Updates: Ensure all network management software, firewall software, and file-sharing software are up-to-date. Regular updates not only provide new features but also fix any known bugs and vulnerabilities.
- Hardware Checks: Conduct regular checks of network hardware like routers, switches, and Ethernet cables for any signs of damage or wear. Replace any faulty components promptly.
- Security Checks: Regularly scan the network for potential security threats. Make sure that firewall settings are updated, and all devices in the network have adequate security measures in place.
- Backup and Recovery: Regularly backup critical files and configurations. In the event of a severe system failure or data loss, having a recent backup can significantly reduce downtime.
- Training: Regularly train the users of the laser-cutting machines on how to properly use the network and software tools. This can reduce user-related issues and improve the overall efficiency of the operations.
By adhering to these maintenance guidelines, you can ensure a smoothly functioning network of laser-cutting machines with efficient software processes.
Summary
Setting up, managing, and maintaining a network of laser-cutting machines might seem like a daunting task, but with the right knowledge and tools, it’s a task that can be handled efficiently. Ethernet connectivity has proven to be a game-changer, enabling businesses to enhance productivity by linking multiple machines together.
From selecting the right hardware and software components, configuring the network, to managing file sharing and jobs, each step plays a crucial role in creating a successful machine network. Maintaining the network – including regular monitoring, timely updates, security checks, and user training – ensures a smoothly functioning system.
Remember, while technology can streamline processes and enhance productivity, it also requires regular care and attention. Whether it’s a small business or a large manufacturing facility, a well-maintained network of laser-cutting machines can pave the way for improved efficiency, productivity, and, ultimately, a thriving business.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into setting up and maintaining a network of laser-cutting machines. With these steps, you are now equipped to optimize your operations and take your laser cutting to the next level. Happy cutting!
This blog post was sponsored by RPMC Lasers - a Leading US supplier of various laser technologies