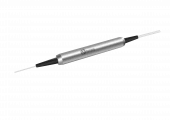
Description
The GKER Photonics 445-2100 nm Special Wavelength Coupler (GK-SMC Series) is a highly versatile optical component designed to meet the demands of modern optical communication and laser systems. Covering a broad wavelength range from 445 nm to 2100 nm, this coupler is engineered for applications requiring precise power monitoring, signal splitting, and wavelength management.
With its low polarization dependent loss (PDL) and minimal excess loss, the coupler ensures optimal signal integrity and performance across various wavelengths. Available in multiple coupling ratios from 1/99 to 50/50, it provides flexibility in power distribution, catering to a wide array of configurations and system requirements.
Built to withstand challenging environmental conditions, the GKER Photonics coupler offers excellent thermal stability and high optical power handling capability, making it ideal for high-power laser systems, fiber optic communication networks, and advanced testing instruments. The coupler can be customized with various connector types and fiber options, ensuring compatibility with different systems and applications.
Whether you are working in coherent communication, fiber laser development, or optical testing, the GKER Photonics Special Wavelength Coupler delivers reliable, high-performance solutions tailored to your needs.
445 - 2100 nm Special Wavelength Coupler
Specifications
| Type: | Other / Not Specified |
|---|---|
| Configuration: | 1x2 |
| Splitting Ratio: | Other / Not specified |
| Wavelength: | 445 nm |
| Fiber Type: | SMF-28e |
| Connector Type: | Other / Not specified |
| Housing Material: | Other / Not specified |
| Center Wavelength (λc): | 488,532,635 780,830 980,1064 1700,2000 nm |
| Operating Wavelength: | λc ± 5 λc ± 10 λc ± 10 λc ± 20 nm |
| Max. PDL: | 0.2 0.2 0.1 0.2 dB |
| Max. Excess Loss: | 0.3 0.3 0.15 0.3 dB |
| Max. Excess Loss For Each Connector: | 1.5 0.7 0.5 0.3 dB |
| Max. Optical Power (Continuous Wave): | 4 W |
| Thermal Stability: | ≤ 0.005 dB/℃ |
| Min. Return Loss: | 50 dB |
| Min. Directivity: | 50 dB |
| Fiber Type: | Singlemode Fiber - |
| Operating Temperature: | - 40 to + 75 ℃ |
| Storage Temperature: | - 40 to + 85 ℃ |
| Coupling Ratio: | 1/99 2/98 5/95 10/90 20/80 30/70 40/60 50/50 % |
Features
- Wide Wavelength Range: Operates across 445 nm to 2100 nm
- Low Polarization Dependent Loss: Maximizes signal integrity with PDL as low as 0.1 dB
- High Power Handling: Supports up to 4 W continuous wave optical power
- Versatile Coupling Ratios: Available from 1/99 to 50/50 for precise power distribution
- Excellent Thermal Stability: Maintains performance with thermal stability ≤ 0.005 dB/℃
- High Stability and Reliability: Ensures consistent operation under varying environmental conditions
- Compact and Durable Design: Designed for long-lasting use in demanding applications
Applications
- Power Monitoring: Ideal for real-time monitoring of optical power levels
- Signal Splitting: Efficiently splits optical signals for distribution across multiple pathways
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM): Facilitates the separation and combination of different wavelengths
- Laser Systems: Supports precise power distribution in fiber laser applications
- Optical Communication Networks: Enhances the performance and reliability of communication systems
- Testing Instruments: Used in advanced optical testing equipment
Frequently Asked Questions
What wavelength range does the GKER Photonics Special Wavelength Coupler support?
What are the typical applications of this coupler?
What coupling ratios are available for this coupler?
How does the coupler handle high optical power?
What is the thermal stability of the GKER Photonics Coupler?
Can this coupler be used in extreme temperature environments?
What types of fibers are compatible with this coupler?
How does the polarization dependent loss (PDL) affect the performance of this coupler?
Is this coupler available with different connector types?
What is the typical insertion loss for different coupling ratios?
Similar Products




Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle